1.What is SEO ?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization.
In plain English: it’s the practice of making your website (or content) easier for search engines like Google to understand, trust, and rank highly when people search for relevant things.
2.How Search Engines Work
Search engines (like Google, Bing, or Yahoo) are tools that help users find information on the internet quickly and accurately. Every time you type a query into a search engine, it scans billions of web pages to show the most relevant results within seconds.
Behind the scenes, search engines follow a structured process to discover, understand, and rank web content. This process mainly involves three key steps:
3.History of SEO
1. Early Stage of SEO (1990–1997)
The history of Search Engine Optimization began in the early 1990s when the internet was still new and search engines like Archie, AltaVista, and Yahoo were commonly used. During this period, website owners manually submitted their web pages to search engines. Rankings mainly depended on keywords and meta tags, which led to excessive keyword stuffing and easy manipulation of search results.
2. Introduction of Google (1998–2003)
In 1998, the launch of Google brought a major change inSearch Engine Optimization . Google introduced the PageRank algorithm, which evaluated websites based on the number and quality of backlinks. This shift reduced the sole dependence on keywords and increased the importance of website authority and content relevance.
3. Algorithm Improvement Phase (2004–2010)
Between 2004 and 2010, search engines started improving their algorithms to fight spam and low-quality websites. Keyword stuffing and irrelevant content were penalized, and Search Engine Optimization became a more structured and professional practice focused on relevant content and natural link building.
4. Major Google Algorithm Updates (2011–2015)
This period is considered a turning point in Search Engine Optimization history. Google launched major updates such as Panda, which targeted low-quality and duplicate content, and Penguin, which penalized spammy backlinks. The Hummingbird update further improved Google’s ability to understand search intent, shiftingSearch Engine Optimization towards user-focused content.
5. Mobile and User Experience Era (2016–2019)
With the rapid growth of mobile usage, Google introduced mobile-first indexing. Website speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall user experience became important ranking factors. Voice search also gained popularity during this time.
6. Modern SEO and AI Era (2020–Present)
In recent years,Search Engine Optimization has become highly advanced with the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Algorithms like RankBrain and BERT help search engines understand context and user intent more accurately. Today, seo emphasizes E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) and focuses on providing helpful, high-quality content to users.
4.Importance of seo
1. Increases Website Visibility
seo helps a website appear higher in search engine results. When a website ranks on the first page of Google, more people can find it easily, which increases visibility and online presence.
2. Drives Organic Traffic
One of the biggest advantages of Search Engine Optimization is that it brings free and organic traffic to a website. Unlike paid ads, seo allows users to reach your site naturally through search results, making it cost-effective in the long run.
3. Builds Trust and Credibility
Websites that rank higher on search engines are generally considered more trustworthy by users. Good practices, such as quality content and secure websites, help build credibility and brand trust.
4. Improves User Experience
Search Engine Optimization is not only about search engines but also about users. Fast loading pages, mobile-friendly design, clear navigation, and useful content improve the overall user experience, which helps retain visitors.
5. Supports Business Growth
Search Engine Optimization helps attract potential customers who are actively searching for products or services. This increases leads, conversions, and sales, making seo an important tool for business growth.
6. Long-Term Results
Unlike paid advertising, provides long-term benefits. Once a website gains good rankings, it can continue to receive traffic for a long time with regular optimization and updates.
5.Organic vs Paid Traffic
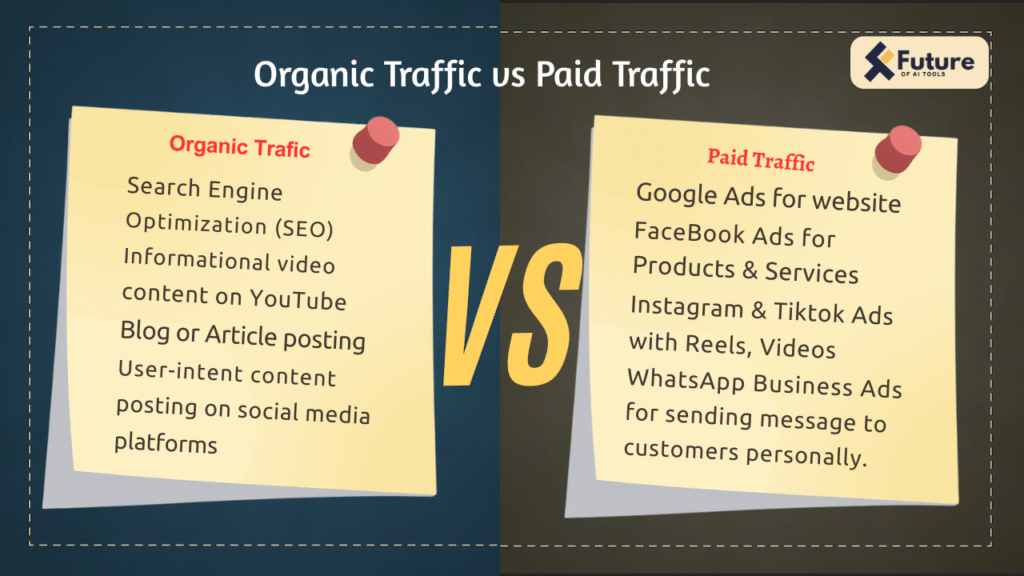
Organic Traffic refers to visitors who come to a website naturally through search engine results without any paid advertisements. This type of traffic is generated mainly through seo by optimizing website content, keywords, and overall user experience. Organic traffic is considered more trustworthy because users find the website on their own while searching for information. Although it takes time to build, organic traffic is cost-effective and provides long-term results.
Paid Traffic refers to visitors who come to a website through paid advertisements such as Google Ads, social media ads, or sponsored links. In this case, businesses pay for each click or impression to attract visitors quickly. Paid traffic delivers instant results and is useful for promotions, new launches, or competitive keywords. However, once the advertising budget stops, the traffic also stops.
Both organic and paid traffic are important in digital marketing. Organic traffic is ideal for long-term growth and credibility, while paid traffic is useful for quick visibility and immediate results. A balanced strategy using both can provide the best outcomes.
If you want, I can also write this as a comparison table, exam answer, or very simple language version.
6.White Hat, Black Hat & Grey Hat Search Engine Optimization
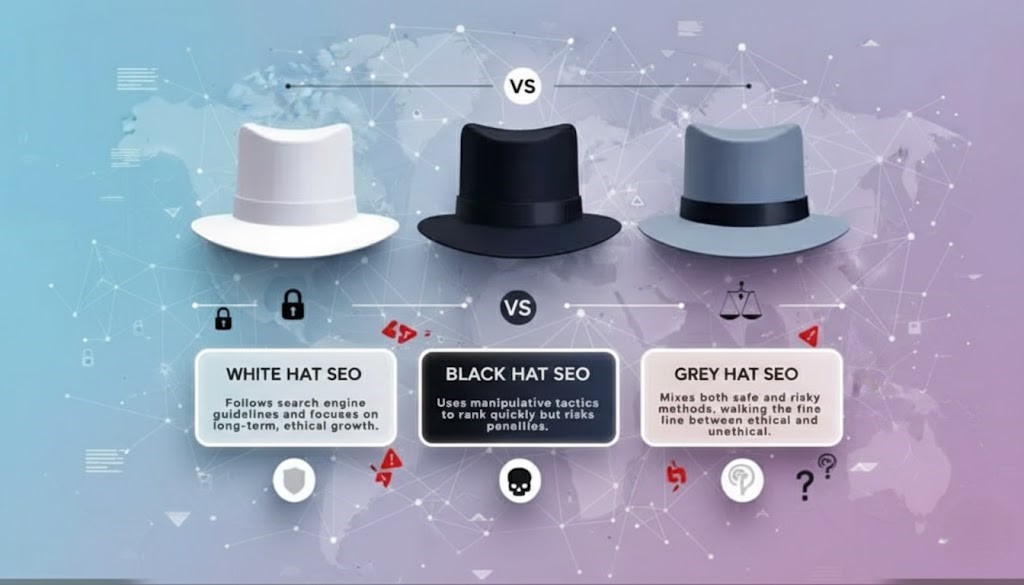
White Hat SEO
White Hat SEO refers to ethical SEO techniques that follow search engine guidelines and focus on providing value to users. It includes creating high-quality and relevant content, using keywords naturally, improving website speed and mobile-friendliness, and building organic backlinks. White Hat seo takes time, but it delivers safe, reliable, and long-term results.
Black Hat seo
Black Hat Search Engine Optimization involves unethical techniques used to manipulate search engine rankings quickly. These techniques include keyword stuffing, hidden text, cloaking, spammy backlinks, and duplicate content. Although Black Hat Search Engine Optimization may give fast results, it carries a high risk of penalties, and the website can be de-indexed or banned by search engines.
Grey Hat
Grey Hat SEO lies between White Hat and Black Hat SEO. It includes practices that are not clearly against search engine rules but are also not completely safe. Examples include aggressive link building or automated content. Grey Hat SEO can sometimes produce results, but it always involves risk.
7.On Page SEO (Complete)
1.On-Page SEO

On-PageSearch Engine Optimization is the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in search engines. It focuses on improving content, HTML, and user experience so search engines understand the page and users can navigate it easily.
2. SEO Friendly URL
An Search Engine Optimization -friendly URL is a short, readable, and descriptive web address that clearly shows the content of the page.
Example: www.example.com/seo-tips is better than www.example.com/page?id=123.
3. Title Tag Optimization
A title tag is the clickable headline that appears in search results. Optimizing it means using the main keyword naturally and keeping it under 60 characters so it is readable and relevant.
4. Meta Description Optimization
A meta description is a short summary of the page shown in search results. Optimizing it involves writing a compelling, keyword-relevant description (around 150–160 characters) to improve click-through rate.
5. Heading Tags (H1–H6)
Heading tags organize content into sections and make it readable.
- H1: Main title (one per page)
- H2–H6: Subheadings for structure and hierarchy
They help users and search engines understand the page structure.
6. Keyword Placement
Using keywords in strategic places like the title, headings, first 100 words, and naturally throughout the content to show relevance without keyword stuffing.
7. Content Optimization
Content optimization means creating high-quality, relevant, and valuable content for users while making it search-engine friendly. It includes proper formatting, headings, keywords, and readability.
8. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is identical or very similar content on multiple pages of a website or across websites. It can harm Search Engine Optimization because search engines may not know which page to rank.
9. Image Optimization
Optimizing images improves page load speed and accessibility. This includes compressing images, using correct file names, and adding ALT text.
10. ALT Text
ALT text is a short description of an image used by search engines and screen readers. It helps with image Search Engine Optimization and accessibility.
Example: <img src=”seo-guide.jpg” alt=”SEO guide for beginners”>
11. Internal Linking
Internal linking is linking one page of your website to another. It helps users navigate the site and helps search engines crawl and index pages better.
12. External Linking
External linking is linking your content to other high-authority websites. It shows search engines that your content is reliable and well-researched.
13. Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text in a link. Using descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text improves SEO and helps users understand the linked page.
14. Schema Markup (Basic)
Schema markup is structured data added to HTML that helps search engines understand the content better and display rich results (like stars, ratings, FAQs).
15. Content Freshness
Content freshness means updating old content regularly or adding new information. Fresh content ranks better because search engines value relevant and up-to-date information.
16. E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)
E-E-A-T is a Google ranking factor that evaluates the quality and credibility of content and the website. Pages with high E-A-T are considered trustworthy and authoritative, especially for health, finance, and education topics.
8.Content SEO (Complete )
1. Content SEO
Content SEO is the practice of creating and optimizing content so that it ranks higher on search engines. It focuses on making content relevant, valuable, and easy for both users and search engines to understand.
2. What is Content Marketing
Content marketing is the strategy of creating and sharing valuable content (like blogs, videos, guides) to attract, engage, and retain an audience. Unlike ads, it focuses on building trust and long-term relationships with users.
3. SEO Content Writing
SEO content writing is the process of writing content specifically for search engines while keeping it readable for humans. It includes using keywords naturally, proper headings, meta tags, and optimizing for ranking.
4. Blog Writing for SEO
Blog writing for SEO means creating informative, keyword-optimized blog posts that answer users’ queries. The goal is to rank in search results, drive traffic, and build authority.
5. Article Optimization
Article optimization is improving existing content to make it more search-engine friendly. This includes adding keywords, headings, internal links, meta description, images, and ensuring readability.
6. Content Length
Content length refers to the word count of an article or page. Longer content often performs better in search results if it is detailed, relevant, and high-quality. However, quality is more important than just word count.
7. Keyword Density
Keyword density is the percentage of times a keyword appears in the content compared to total words. It should be natural and not overstuffed, usually around 1–2% for best SEO results.
8. Plagiarism Free Content
Plagiarism-free content is original content that is not copied from other sources. Search engines penalize duplicate content, so originality is crucial for SEO.
9. AI Content & SEO
AI content refers to content created using AI tools. It can save time, but it must be checked for accuracy, uniqueness, and readability. Google values helpful, human-like content over purely AI-generated text.
10. Content Updating Strategy
Content updating strategy is the plan to regularly revise and improve existing content. This keeps it fresh, accurate, and relevant, which helps maintain or improve search rankings over time.
FAQs
1. What is SEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the practice of optimizing a website so that it ranks higher in search engines, attracts relevant traffic, and improves online visibility.
2. What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO involves optimizing individual web pages by improving content, title tags, meta descriptions, headings, URLs, internal links, images, and other elements to make them search-engine friendly.
3. What is Content SEO?
Content SEO focuses on creating high-quality, relevant, and optimized content that answers users’ queries and helps the website rank higher in search results.
4. What is the difference between Organic and Paid Traffic?
Organic traffic comes naturally through search engine results without paying for ads, while paid traffic is generated by advertisements such as Google Ads or social media campaigns.
5. What are White Hat, Black Hat, and Grey Hat SEO?
- White Hat SEO: Ethical SEO techniques that follow search engine guidelines.
- Black Hat SEO: Unethical techniques that manipulate rankings and risk penalties.
- Grey Hat SEO: Techniques that are somewhere in between; not clearly allowed but not strictly forbidden
Conclusion
SEO is the most effective way to increase a website’s visibility and attract the right traffic. Through On-Page and Content SEO, high-quality and optimized content is created. Websites like futureofaitools.in use these strategies to provide useful information and maintain a strong online presence. Proper SEO techniques and user-focused content ensure long-term growth and credibility.